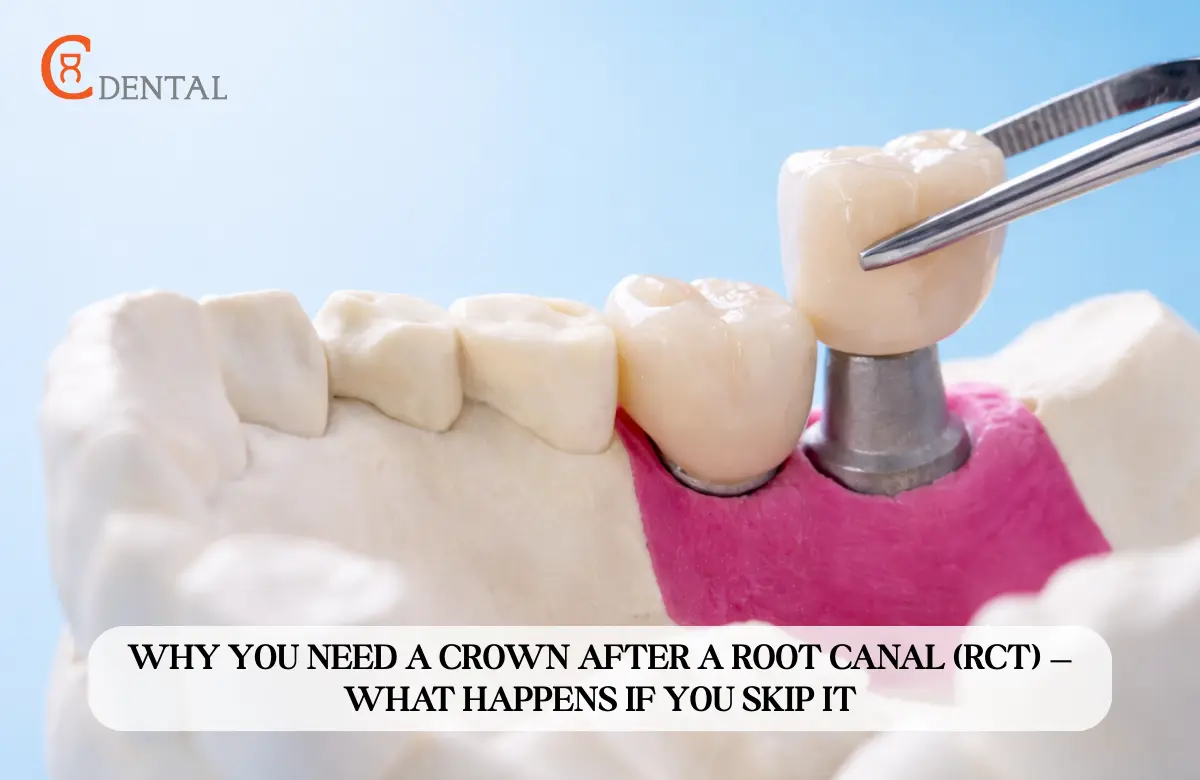
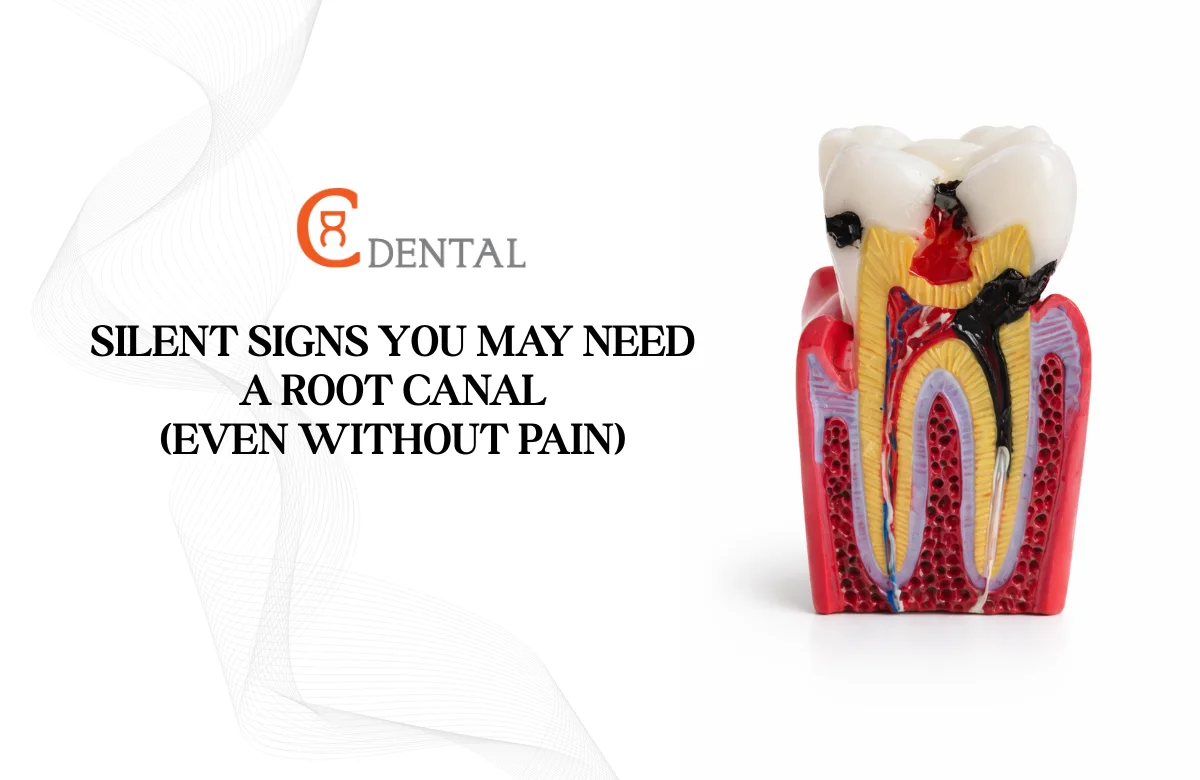
A root canal treatment (RCT) is a widely performed dental procedure designed to save a severely decayed or infected tooth. While a root canal effectively removes pain and infection, it also leaves the treated tooth structurally weaker and more vulnerable to fracture over time.
This often leads patients to ask common questions like, “Is a crown necessary after a root canal?” or “What happens if I do not get a crown after RCT?”
In this article, we explain why a dental crown is usually recommended after root canal treatment, the potential risks of skipping the crown, and the long-term benefits of protecting and restoring your tooth with a crown so that you can make an informed decision about your oral health.
What Happens to a Tooth After a Root Canal?
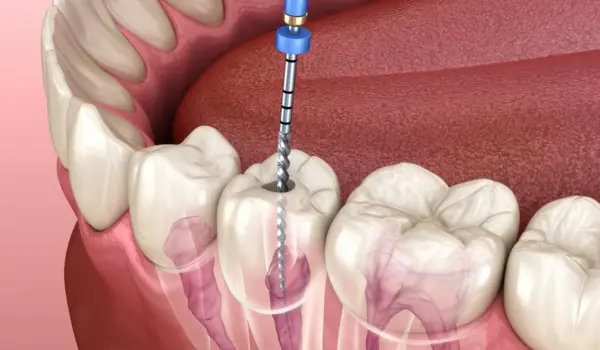
During a root canal, the dentist removes the infected or inflamed pulp from inside the tooth. While this procedure saves the tooth from extraction, it also removes the natural nerves and blood supply, leaving the tooth dry and brittle.
Without the pulp, the tooth loses some of its natural flexibility and strength. Daily activities like chewing or grinding can put stress on the remaining structure, increasing the risk of cracks, fractures, and eventual tooth failure. Even if the tooth looks healthy on the surface, its internal structure is compromised and needs additional protection.
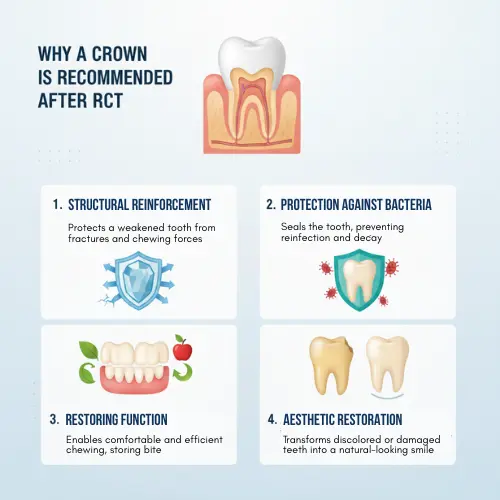
Why a Crown Is Recommended After RCT?
Crowns serve as a protective and restorative cap for a root canal–treated tooth. They offer several important benefits:
1. Structural Reinforcement
A crown covers the weakened tooth, distributing chewing forces evenly and preventing cracks or fractures. This is especially important for molars and premolars, which endure heavy bite pressure.
2. Protection Against Bacteria
Even after a successful root canal, tiny cracks or incomplete seals can allow bacteria to enter. A crown creates a protective barrier, reducing the risk of reinfection.
3. Restoring Function
Crowns restore normal chewing ability and bite alignment, allowing you to eat and speak comfortably.
4. Aesthetic Restoration
For front teeth, a crown can restore the tooth’s natural appearance, cover discoloration, and improve your smile.
What Happens If You Skip a Crown After RCT?
Some patients consider skipping the crown to save money or because the tooth “feels fine.” However, this can have serious consequences:
Higher Risk of Fracture
A tooth without a crown is more likely to crack or break, even during normal chewing. Once a fracture extends below the gumline, the tooth often becomes non-restorable and may need to be extracted.
Reinfection and Decay
A filling alone may not protect the entire tooth. Gaps or tiny cracks can let bacteria enter, causing reinfection, further decay, and the need for retreatment or extraction.
Loss of Tooth Integrity
Over time, the untreated tooth may gradually chip or wear down. This silent deterioration can lead to more complex and costly dental work later.
Potential Tooth Loss and Higher Costs
If the tooth fractures or becomes reinfected beyond repair, extraction may be necessary. Replacing the tooth with a bridge, denture, or implant is far more expensive and invasive than placing a crown in the first place.
Situations Where a Crown May Not Be Necessary
Not every RCT, treated tooth requires a crown. Examples include:
- Front teeth (incisors/canines) that face minimal chewing pressure
- Teeth where minimal structure was removed for the root canal
- Cases where a composite filling or onlay is sufficient to restore function
Even in these cases, a dentist must carefully evaluate bite forces and remaining tooth structure to determine the best restoration option.
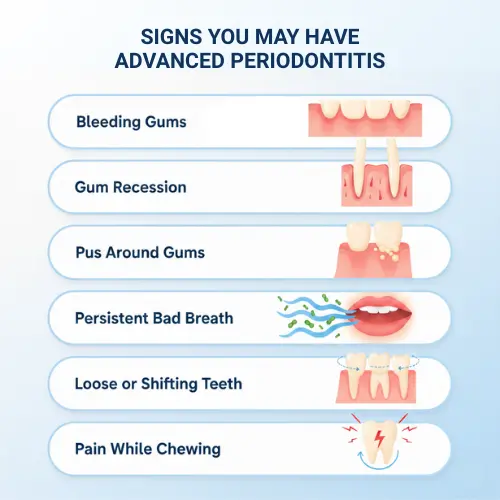
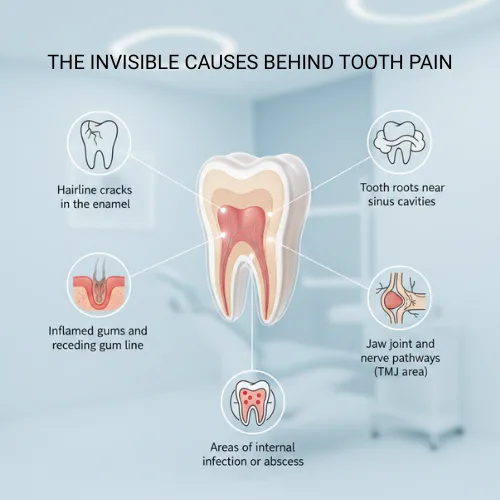
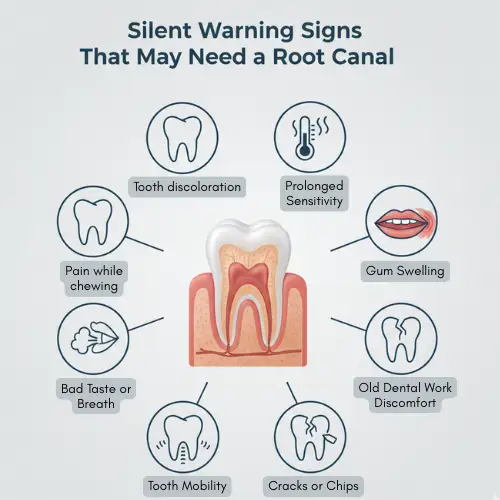
Does Your Root Canal Tooth Need a Crown? Watch for These Signs:
- Cracks or fractures – Even small ones can weaken the tooth.
- Darkening or discoloration – A sign the tooth may be brittle.
- Ongoing sensitivity – Pain when biting or with temperature changes.
- Large fillings or missing tooth structure – Less natural support makes it prone to breaking.
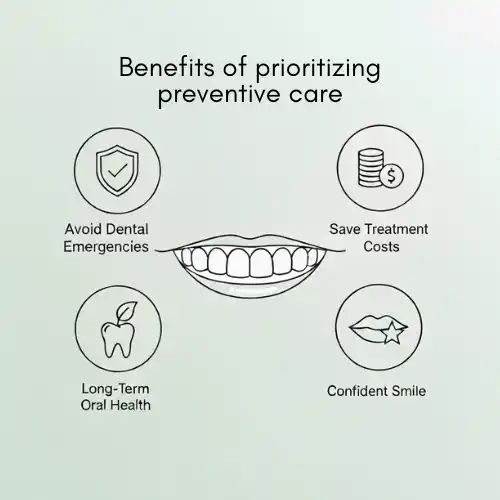
How a Crown Protects Your Root Canal Tooth for the Long Haul?
A crown does more than just look nice—it strengthens and protects your tooth:
- Stops cracks and fractures – Shields the tooth from everyday biting and chewing.
- Prevents reinfection – Seals the tooth to keep bacteria out.
- Restores proper function – Lets you bite and chew without worry.
- Keeps your smile natural – Looks and feels like a real tooth.
With the right care, a crowned tooth can last for decades, keeping your smile healthy and strong.
Best Crown Materials for Your Root Canal Tooth
After a root canal, choosing the right crown is crucial for strength, function, and appearance. Here are the most common options:
- Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) – Combines durability with a natural look, ideal for back teeth that endure heavy chewing.
- All-Ceramic or Zirconia – Offers the best aesthetics and is highly biocompatible, perfect for front teeth.
- Composite Crowns – Affordable and effective as a temporary or short-term solution.
Your dentist will recommend the best material based on your tooth’s position, bite pressure, and cosmetic needs, ensuring long-lasting protection and a natural smile.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A: Ideally, a crown should be placed within a few weeks after RCT. Delaying it increases the risk of cracks, fractures, or reinfection of the tooth.
A: In some cases, especially front teeth with minimal chewing pressure, a tooth may last without a crown. However, most back teeth require a crown to prevent breakage and long-term failure.
A: A filling alone does not provide sufficient strength for most root canal-treated teeth. Crowns offer full coverage and protection that fillings cannot, especially for molars and premolars.
A: If the tooth fractures below the gumline, it may become non-restorable and require extraction. This often leads to more expensive treatments like implants or bridges.
A: With proper oral hygiene and regular dental checkups, a crown placed after a root canal can last 10 to 20 years or even longer.
Conclusion
A root canal preserves your natural tooth, but it also leaves it more fragile. A crown reinforces and protects the tooth while restoring full function and a natural appearance. Skipping a crown might save money upfront, but it dramatically increases the risk of cracks, reinfection, and even tooth loss.
The best way to safeguard your root canal investment is to get a crown promptly and follow your dentist’s care instructions.
👉 Don’t wait—schedule your crown consultation today to protect your smile for years to come!
References
- Why Do You Need a Crown after a Root Canal– Pure Dentistry
- Do I Need A Crown After A Root Canal?– Fab Dental
- Why Some Teeth Need Crowns After Root Canals– Pittsfield Dental
- What Happens If You Skip the Crown After an RCT?– Prime Dental Clinic
- What Happens If You Don’t Get a Crown After a Root Canal Treatment?– Timberlands Dental Clinic
- What happens after a Root Canal?–Eastern Idaho Endodontics
Please subscribe to our social channels for updates related to dental care and oral health.
Instagram: cdental2025
Facebook: CDental
YouTube: C-Dental Clinic